Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hands and wrists, causing pain, numbness, and tingling sensations. It's a result of pressure on the median nerve, which controls sensations and movements in the thumb and first three fingers. While CTS can develop over time, it's important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to help manage and alleviate its effects.
What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist that houses the median nerve and tendons responsible for moving the fingers. When this tunnel becomes compressed, the pressure on the median nerve can result in a range of uncomfortable and debilitating symptoms. CTS is often associated with repetitive hand movements, particularly those involving the wrist in flexion or extension, but it can also be linked to other factors, including underlying health conditions [Wipperman & Penny, 2024; Wipperman & Goerl, 2016; Malakootian et al, 2023].
What are the Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Several factors contribute to the development of CTS, including:
What are the Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can manifest in various ways, and symptoms often start gradually. Common signs include:
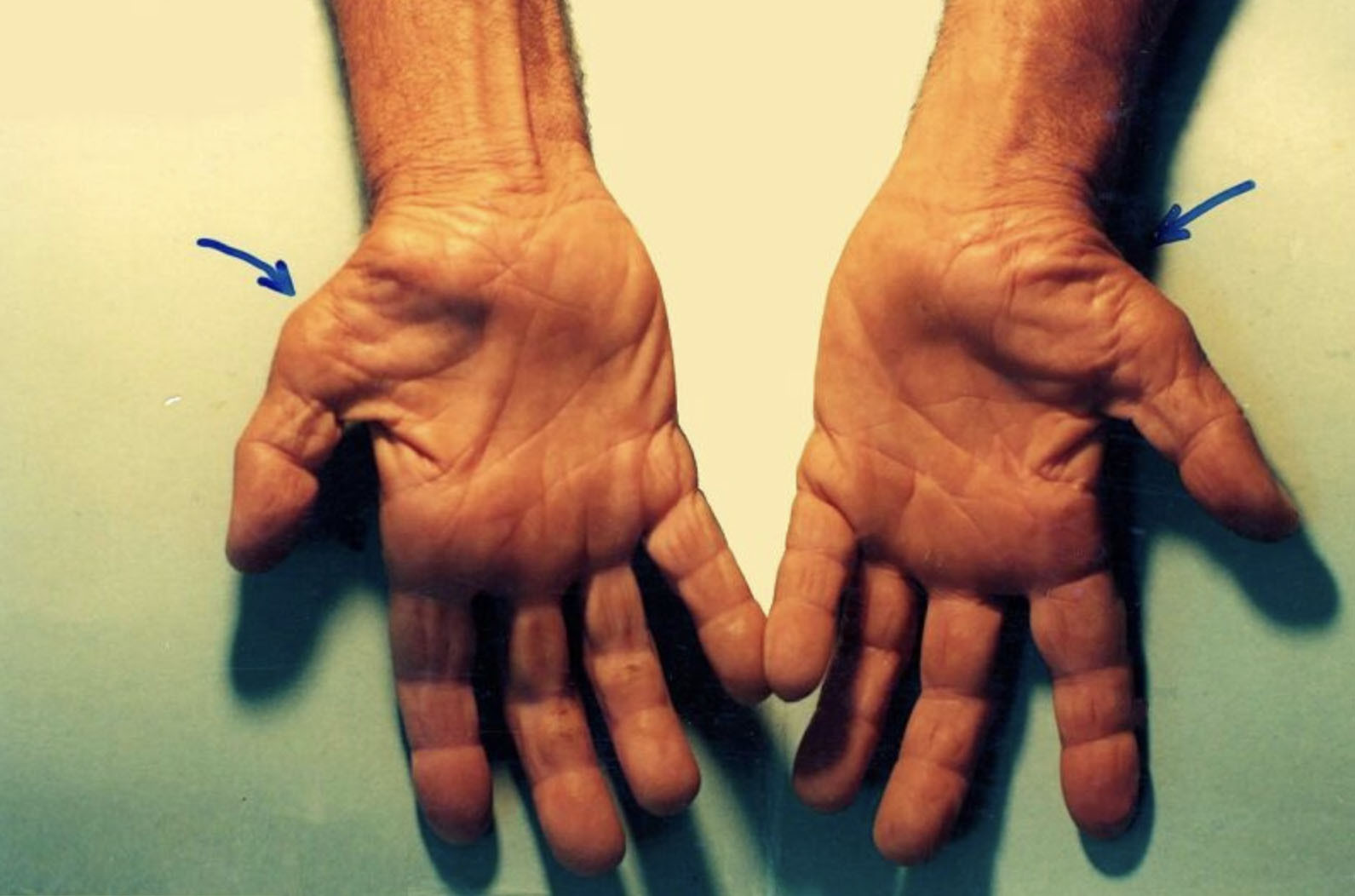
What are the Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
If you suspect you have CTS, it’s essential to seek medical advice early on to prevent further damage to the median nerve. There are several treatment options available, depending on the severity of the condition:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
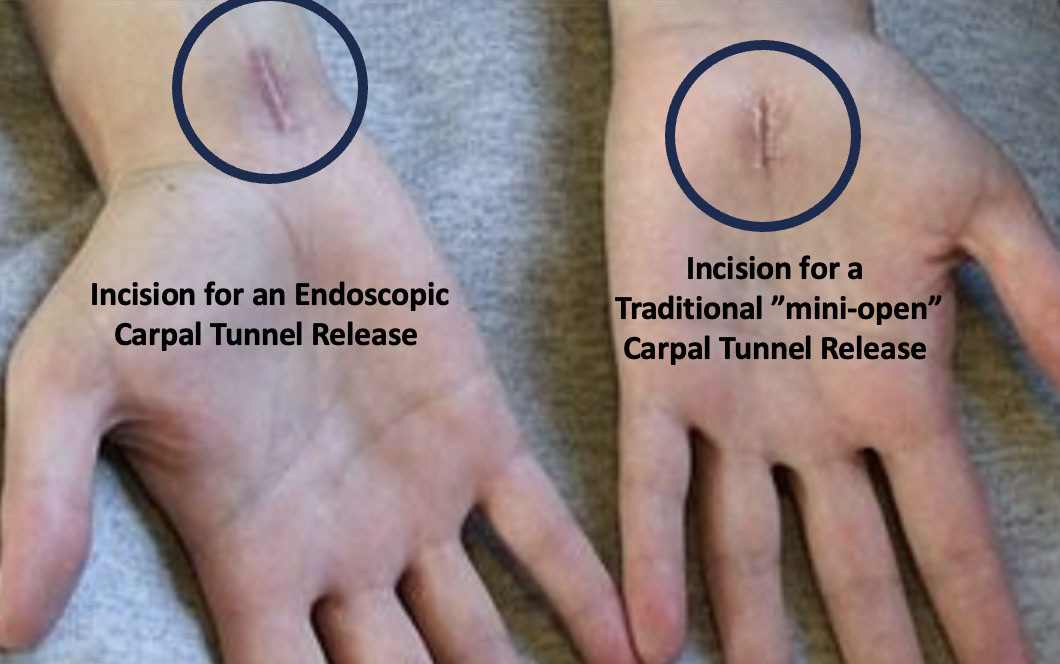
2. Surgical Treatment
In severe cases of CTS, or when conservative treatments fail to
provide relief, surgery may be necessary. The most common surgical
procedure for CTS is called carpal tunnel release, which involves cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel to reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Prevention Tips
While some risk factors for CTS, such as genetics or underlying medical conditions, cannot be controlled, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:

Final Thoughts
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, but with early intervention and proper management, most individuals can find relief. If you're experiencing any symptoms of CTS, it’s important to seek professional advice to determine the best course of action. With the right treatment plan, you can alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent the condition from progressing.
Schedule a consultation at:
(781) 591-7855
20 Walnut St
Suite 14
Wellesley MA 02481
References:
Discover how PRP injections may outperform traditional treatments for mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome. Backed by a 2020 meta-analysis of clinical trials.
Read MoreCarpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is one of the most common nerve-related conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide—especially those who spend long hours typing, using tools, or performing repetitive hand
Read More