
How is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosed
The following is a summary of the 2007 American Academy of Orthopedic Surgery (AAOS) guidelines for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome (Keith et al.)
History
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome should begin with a history. Symptoms often include numbness, tingling, burning or weakness in the hand
The duration of symptoms can be variable and symptoms within the median nerve distribution (involving the thumb, index, middle and ½ of the ring finger). Typically, symptoms are worse at night when sleeping or when first waking up.
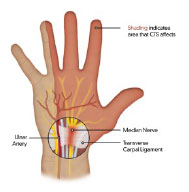
Physical Examination
A sensory and motor examination should be performed, and patients may have decreased sensation in the 1st through 3rd digit and ½ of the 4th digit. Patients may also have decreased sensation in the palm or weakness with pinch, grip or thumb abduction. This may manifest as patients unintentionally dropping objects or clumsiness.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel could be provoked by percussing over the median nerve at the wrist (Tinel’s sign) or increasing pressure within the carpal tunnel by extending the wrist (Phalen et al.; Phalen; Phalen and Kendrick).
Electordiagnostic Studies
Electrodiagnostic studies include electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies. This test measures the strength and speed of impulses along the nerve, and can show evidence of nerve injury. Electrodiagnostic studies have limitations (David & Green; Wang et al.), including that they are can lead to over diagnosing asymptomatic carpal tunnel syndrome. The AAOS guidelines recommend only obtaining electrodiagnostic tests if there is a clinical suspicion of carpal tunnel syndrome and surgical management is being considered (Keith et al.).
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound can be used to measure the cross-sectional area of the median nerve at the wrist and has been correlated with electrodiagnostic studies, and can also be used to confirm the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (Ting et al.; Wessel et al.).

References
David P, Green M. Green's Operative Hand Surgery. 5th ed. Vol One. Elsevier; 2005.
Keith MW, Masear V, Chung KC, et al. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Clinical Practice Guideline on diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91((10)):2478–2479.
PHALEN GS, GARDNER WJ, LA LONDE AA. Neuropathy of the median nerve due to compression beneath the transverse carpal ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1950 Jan;32A(1):109-12.
PHALEN GS. Spontaneous compression of the median nerve at the wrist. J Am Med Assoc. 1951 Apr 14;145(15):1128-33.
PHALEN GS, KENDRICK JI. Compression neuropathy of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. J Am Med Assoc. 1957 Jun 1;164(5):524-30.’
Ting BL, Blazar PE, Collins JE, et al. Median Nerve Ultrasonography Measurements Correlate With Electrodiagnostic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Severity. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27((1)):e17–e23.
Wang WL, Buterbaugh K, Kadow TR, Goitz RJ, Fowler JR. A Prospective Comparison of Diagnostic Tools for the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 2018;43((9)):833–836. e832.
Wessel LE, Marshall DC, Stepan JG, et al. Sonographic Findings Associated With Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 2019;44((5)):374–381.
Discover how PRP injections may outperform traditional treatments for mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome. Backed by a 2020 meta-analysis of clinical trials.
Read MoreCarpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is one of the most common nerve-related conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide—especially those who spend long hours typing, using tools, or performing repetitive hand
Read More